Introduction
JavaScript is a scripting programming language. We can say JavaScript as client-side, interpreted and server-side programming language. Js for creating and controlling dynamic websites. language.
JavaScript was founded by Brendan Eich in 1995. Javascript is the third layer of web technologies. The inspiration behind the js is java. It allows you to implement complex features and actions in your webpages. Js provides js libraries that provide functional attributes in webpages. It is the backbone of the web. This program is able to execute on servers and browsers. Js is platform-independent. Js is very secure. It works with Html and CSS. Js has exception handling. This means it is easy to find the error.
JavaScript is not java. As it gets upgraded, it becomes a fully independent language. It has its own features called ECMA Script. ECMA Script has its different versions. You must get familiar with HTML, CSS to use Js. A scripting language tells the computer applications what to do. Js is unique. It has full integration with HTML and CSS. Js is better in memory management. Angular, Vue, Ember, Metor, Node, Polymer, Aurelia, Mithril, Backbone..etc are some frameworks of Js. It provides proper backend programming.
JavaScript framework is an application framework. The coders can change the functionality of the code and use them for their personal accessibility. One of the features of js is that it often stores values in variables. Client-side js has many APIs available. Javascript provides its own APIs which is Application Programming Interface. APIs are used for providing an interface between user and client. It is often used for saving and retrieving the data from the server. The client posts some information. And the user gets the available information.
History of JavaScript
Brendan Eich, a programmer at Netscape Communications, introduced JavaScript in 1995 to enhance the interaction of webpages. Originally termed Mocha, it was eventually renamed LiveScript and then JavaScript—a marketing ploy to capitalize on Java’s success, despite the fact that the two languages are unrelated.
Netscape Navigator 2.0 introduced JavaScript in December 1995, allowing developers to control the Document Object Model (DOM) and respond to user events. As its popularity rose, ECMA International standardized it in 1997 as ECMAScript (ES), with ES1 being the initial edition.
The possibilities of JavaScript were limited for many years until the rise of AJAX (Asynchronous JavaScript and XML) in the early 2000s, which permitted dynamic content loading without page reloads revolutionizing web apps like Gmail and Google Maps..
Node.js was released in 2009, allowing JavaScript to run on servers and increasing its reach beyond the web browser. The key turning point occurred in 2015, when ES6 (ECMAScript 2015) introduced current features such as let, const, arrow functions, classes, and modules.
Today, JavaScript is the most extensively used programming language in the world, serving as the foundation for the contemporary web. It has progressed from simple browser scripts to a robust, multi-purpose language used throughout the development stack.
Why JavaScript is important
- Runs in all major browsers without plugins
- Enables dynamic content and user interaction
- Forms the core trio of web development with HTML and CSS
- Works across both client-side and server-side
- Used in mobile, desktop, and even IoT development
Features of JavaScript
- Object based scripting programming language.
- Client-side technology and exception handelling.
- DOM Manipulation.
- Validating User’s input.
- Handels Date and time.
- Platform independent.
- Browser Compatible.
- User friendly and inbuilt functions.
JS Use Cases
1. Web Development (Frontend)
- DOM Manipulation
- Event handling
- Animations
- AJAX calls for dynamic content
- SPA (Single Page Applications) using React, Vue, or Angular
2. Web Development (Backend)
- Server-side scripting with Node.js
- APIs and microservices
- Real-time apps with Socket.io
3. Mobile App Development
- Frameworks: React Native, Ionic, NativeScript
4. Desktop Applications
- Build cross-platform apps using Electron (e.g., VSCode, Slack)
5. Game Development
- 2D/3D games using Phaser, Three.js, or Babylon.js
6. Automation & Scripting
- Task runners (e.g., Gulp)
- Browser automation via Puppeteer
JavaScript ecosystem
| Type | Frameworks |
|---|---|
| Frontend | React, Angular, Vue, Svelte |
| Backend | Node.js, Express, NestJS |
| Testing | Jest, Mocha, Cypress |
| Build Tools | Webpack, Parcel, Vite |
| Mobile | React Native, Ionic |
Simple JavaScript Code
Ways of adding js to your page
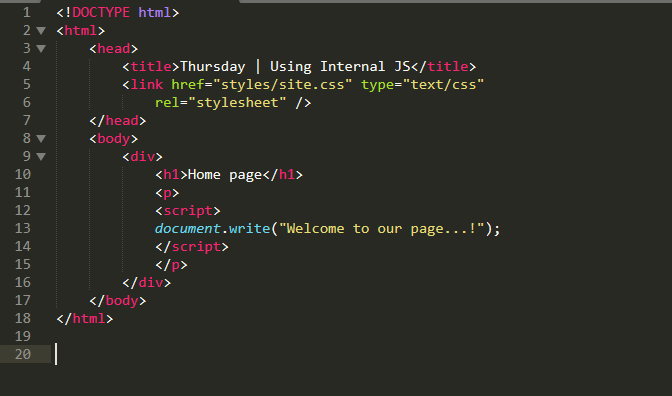
Internal Script
Internal scripts are directly added inside the Html source code.
External Script
In the external script, the code is written separately. The link of that separate script is added to the Html page.

Js Requirements
- Code editors like Atom, Brackets, Webstorm, Sublime-text..etc are required.
- Browsers like Google Chrome, Mozilla firefox..etc. are required.
- If you want to use frameworks you can simple download it.


