Introduction
List comprehension is an effective way to create lists by writing a single line of code. It offers a shorter syntax for creating lists.
List comprehension is more time-efficient and space-efficient than loops. It requires few lines and makes the code more readable. We must use for a keyword while using list-comprehension and if keyword when necessary.
The syntax for list – comprehension.
new_data = [item for item in data]
Examples
number = [1, 2, 3, 4]
new_list = []
for n in number:
add_1 = n + 1
new_list.append(add_1)
print(new_list)
output
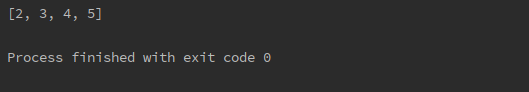
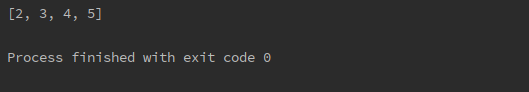
Instead of writing the above code, we can write the same code in a few line that provide the same output.
number = [1, 2, 3, 4] result = [item + 1 for item in number] print(result)
output
list comprehension using if
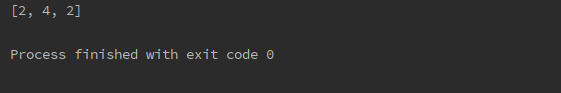
This code prints the number is divisible by 2.
num = [2, 5, 4, 2, 1] even = [item for item in num if item % 2 == 0] print(even)
output