Introduction
A network topology refers to the physical and logical arrangement of nodes and connections in a network. Each node is connected with each using networking devices.
A network topology describes how the network components such as routers, switches, repeaters, computers etc., are arranged in relation to each other and how the data transfer between them. Network topology affects many aspects of network functionality including data transfer speeds, network efficiency, and network security. There is different network topology with its advantages and disadvantages.
When it is about network topology, it has two types. Physical and logical topology. A physical topology describes the physical placement of nodes in each component in a network. A logical topology describes how data flows through the network and how devices are interconnected with each other.
Types of network topology
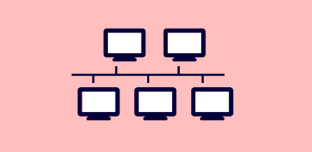
Bus topology
In this topology, all the devices are connected to a single cable that acts as a backbone of the network.
Advantages
- Simple and cost effective to implement.
- Easy to install and configure.
- Suitable for small networks.
Disadvantages
- Limited cable length and number of stations.
- If the main cable fails, the entire cable fails.
- Difficulty in troubleshooting.
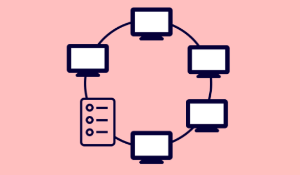
Ring topology
In this topology, all the devices are connected to a centralized hub or switch forming a circular structure.
Advantages
- Easy to install and wire.
- Ease in expansion.
- Fault detection, add and remove parts.
Disadvantages
- Failure of one node causes failure of entire node.
- Difficult to configure.
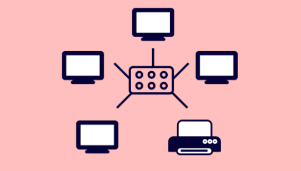
Star topology
In this topology, all the devices are connected to central hub or switch.
Advantages
- Easy to install and implement.
- Easy to expand.
Disadvantages
- Failure of central unit causes failure of entire network.
- Requires more cables.
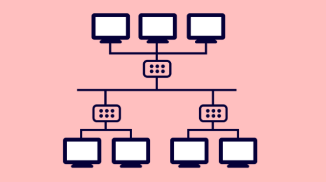
Tree topology
In this topology, each node is connected to each other forming a hierarchy.
Advantages
- Failure of one node does not affect the entire network.
- Node expansion is fast and easy.
- Easy to manage and maintain.
Disadvantages
- High cost due to cabling requirement.
- Difficult to configure.
Mesh topology
In this topology, every node is connected directly to each other.
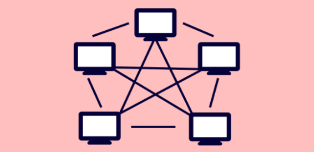
Advantages
- Highly reliable and secured.
- Easy to troubleshoot.
- Multiple paths for data transfer.
Disadvantages
- Expensive to implement.
- Complex to setup and maintain.
Hybrid topology
In this topology, two or more different topology combined together.
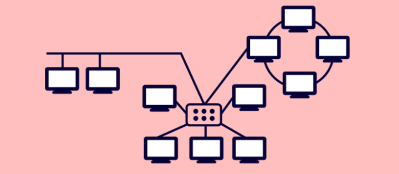
Advantages
- Highly flexible and scalable.
- Reliable due to multiple connection paths.
Disadvantages
- Complex design and implementation.
- Expensive to setup and maintain.
- Difficulty in troubleshooting.



Program iz Pretty! This has been a really wonderful post. Many thanks for providing these details.
Thank you.