Introduction
Frontend and backend development form the two core halves of modern web and app creation. Frontend controls what users experience, and backend controls what the system actually does.
Frontend focuses on how users interact with an interface, while backend handles the data, logic, and infrastructure that make the application work. The frontend is everything users see and interact with directly: layouts, buttons, colors, animations, navigation, and overall user experience. It uses technologies like HTML, CSS, and JavaScript to shape how a website feels and behaves on the screen. If the interface looks bad, loads slowly, or feels confusing, the problem is almost always on the frontend side.
The backend is the engine behind the scenes. It handles data processing, authentication, security, server logic, APIs, and database operations. Backend technologies include Node.js, Python, PHP, Ruby, Java, and databases like MySQL or MongoDB. If something crashes, fails to store information, or behaves inconsistently, that’s usually a backend responsibility. You can specialize in either discipline or develop both skill sets to become a full-stack developer, depending on the depth and direction you want in your career.
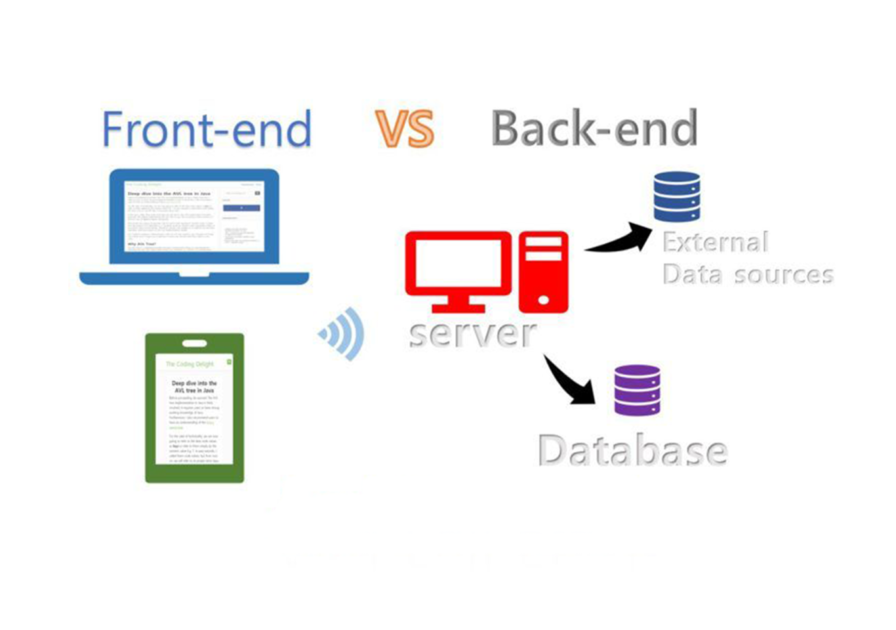
What is Frontend?
Frontend development is the process of building the visual and interactive parts of a website or application that users directly see and engage with. It involves working with HTML, CSS, and JavaScript to create layouts, animations, forms, buttons, and responsive designs that function smoothly across devices. A frontend developer focuses on user experience, accessibility, performance, and clean interface behavior. They ensure pages load quickly, layouts adapt to different screens, and the overall experience feels intuitive and smooth.
Modern frontend development also involves working with frameworks and libraries that speed up development and improve performance. Tools like React, Vue, and Svelte help manage complex interfaces, while build tools such as Vite or Webpack optimize assets behind the scenes. Frontend developers must also consider accessibility, browser compatibility, usability, and design principles so the interface remains functional for all users. Because frontend work directly shapes user experience, it requires a strong understanding of interface behavior, responsive design, and how people interact with digital products.
Responsibilities of a Frontend
- User Interface Implementation: Translating UI/UX designs into functional screens.
- Responsive Engineering: Ensuring consistency across mobile, tablet, and desktop.
- Accessibility: Designing experiences usable by people with disabilities.
- Performance Optimization: Minimizing load times, asset sizes, and re-renders.
- State Management: Handling user interactions and data flow.
- Browser Compatibility: Managing different engines, rendering rules, and standards.
What is Backend development?
Backend development is the discipline responsible for building the server-side logic, databases, APIs, authentication systems, and infrastructure that allow applications to function behind the scenes. Unlike frontend development, which focuses on what users see, the backend handles data flow, business logic, security, and performance. Backend developers work with languages such as Node.js, Python, Java, PHP, and Go, along with databases like MySQL, PostgreSQL, and MongoDB. They design APIs, manage servers, handle user accounts, and ensure data is processed, stored, and delivered correctly.
A strong backend must be secure, scalable, and optimized. It involves understanding server architecture, cloud services, caching, load balancing, and error handling. Backend developers often utilize frameworks and tools such as Express.js (Node.js), Django (Python), Spring Boot (Java), and Laravel (PHP) to streamline their development. Because backend work directly affects reliability and performance, it requires clear thinking, systematic logic, and a strong understanding of how systems behave under real-world load.
Responsibilities of a Backend
- API Development: Building routes, endpoints, and data flow logic.
- Database Architecture: Structuring and storing information efficiently.
- Authentication & Security: Tokens, sessions, encryption, authorization rules.
- Server-Side Logic: Processing payments, managing user accounts, handling form submissions.
- Load Handling & Scalability: Ensuring stability under high traffic.
- System Integration: Connecting email systems, CRMs, payment gateways, and cloud platforms.
Key Differences
| Aspect | Frontend Development | Backend Development |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Controls what users see and interact with | Handles data, server logic, and system functionality |
| Focus Area | User interface, layout, visuals, and usability | Data processing, authentication, APIs, databases, server operations |
| Core Technologies | HTML, CSS, JavaScript, React, Vue, Svelte | Node.js, Python, PHP, Java, Go, MySQL, PostgreSQL, MongoDB |
| Primary Role | Enhances user experience and presentation | Ensures application reliability, security, and performance |
| Tools & Frameworks | React, Vue, Angular, Tailwind CSS | Express.js, Django, Laravel, Spring Boot |
| User Interaction | Directly interacts with the user | Works behind the scenes with no direct user interaction |
| Performance Concern | Visual components, animations, and interface behavior | Server speed, database queries, scalability |
| Output | Design sense, usability, responsiveness, and DOM manipulation | JSON APIs, server responses, database transactions |
| Skills Needed | Design sense, usability, responsiveness, DOM manipulation | Logical thinking, data structures, server handling, security |
| End Goal | Make the interface appealing and intuitive | Make the system stable, efficient, and scalable |
Tools Comparison
| Tool/Resource | Frontend Development | Backend Development |
|---|---|---|
| IDE/Editor | VS Code, Sublime Text, Atom | VS Code, PyCharm, IntelliJ IDEA |
| Version Control | Git, GitHub | Git, GitHub |
| Frameworks | React, Vue.js, Angular | Django, Express.js, Spring Boot |
| Libraries | jQuery, Bootstrap | SQLAlchemy, Hibernate, Mongoose |
| Testing Tools | Jest, Cypress, Selenium | JUnit, PyTest, Postman |
| Design Tools | Figma, Adobe XD, Sketch | N/A (focus is logic & server-side) |
Which is harder?
- Frontend requires strong visual and design sense, creative problem-solving, and understanding how users interact with the interface. Debugging is often faster because errors are visible in the browser.
- Backend demands logical thinking, database knowledge, understanding APIs, server management, and security. Bugs are harder to trace because they are hidden behind the scenes.
- Frontend is easier to start with, but harder to master advanced UX design, animations, and responsive designs. Backend is harder initially due to server architecture, data structures, and security considerations.
- Frontend is complex visually, backend is complex technically. Frontend mistakes are visible, backend mistakes may break the system silently.
- Backend developers often face steeper challenges but are in high demand for scalable systems; frontend developers are crucial for engaging interfaces and user retention
Frontend vs backend workflow
- The product team defines requirements.
- UI/UX team creates wireframes and prototypes.
- The backend team sets up server logic and database architecture.
- Frontend team builds layouts and components.
- Backend exposes API endpoints.
- Frontend consumes those APIs.
- Both teams test integration.
- DevOps deploys to production.
- Performance monitoring begins.