Introduction
Python tkinter is a python interface to the Tk GUI toolkit shipped with python. Python tkinter is very useful and provides a fast and easy way to create GUI app.
Python Tkinter provides a powerful object-oriented interface to the Tk GUI toolkit. With Tkinter you can make windows, buttons, display text, images, and other things. While using it, you must import python tkinter module at first.
from tkinter import * Or import tkinter
All python Tkinter widgets have access to specific geometry management methods, which have the purpose of organizing widgets throughout the parent widget area. Tkinter exposes the following geometry manager classes:
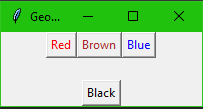
Pack
The geometry manager organizes widgets in blocks before placing them in the parent widget. The possible options can be expanded, fill, and side.
from tkinter import *
root = Tk()
root.title("Geometry Management")
root.geometry("500x500")
frame = Frame(root) #Frame holds all the
frame.pack()
#python tkinter button Widgets
redbutton = Button(frame, text="Red", fg="red")
redbutton.pack( side = LEFT)
greenbutton = Button(frame, text="Brown", fg="brown")
greenbutton.pack( side = LEFT )
bluebutton = Button(frame, text="Blue", fg="blue")
bluebutton.pack( side = LEFT )
bottomframe = Frame(root)
bottomframe.pack( side = BOTTOM )
blackbutton = Button(bottomframe, text="Black", fg="black")
blackbutton.pack( side = BOTTOM)
root.mainloop()
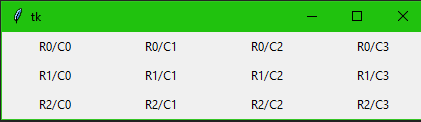
Grid
This geometry manager organizes widgets in a table-like structure in the parent widget. Some possible options are column, row, padx, pady, ipadx, and ipady.
import tkinter
root = tkinter.Tk( )
for r in range(3):
for c in range(4):
tkinter.Label(root, text='R%s/C%s'%(r,c), borderwidth=1 ).grid(row=r,column=c, padx=5 , ipadx=30, pady= 5)
root.mainloop()
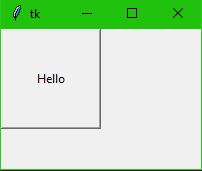
Place
Organizes widgets by placing them in specific position in the parent widget. The possible options can be anchor, border mode, height, width, horizontal and vertical offset in pixels.
from tkinter import * import tkinter.messagebox top = Tk() def helloCallBack(): tkinter.messagebox.showinfo( "Hello Python", "Hello World") B = tkinter.Button(top, text ="Hello", command = helloCallBack) B.pack() B.place(bordermode=OUTSIDE, height=100, width=100) top.mainloop()
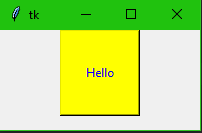
Python tkinter colors
Tkinter represents colors with strings. We can apply colors for objects in our program. There are two general way to specify colors. Hexadecimal and Standard colour.
Some color options
- activebackground − Background color for the widget when the widget is active.
- activeforeground − Foreground color for the widget when the widget is active.
- background − Background color for the widget. This can also be represented as bg.
- disabledforeground − Foreground color for the widget when the widget is disabled.
- foreground − Foreground color for the widget. This can also be represented as fg.
- highlightbackground − Background color of the highlight region when the widget has focus.
- highlightcolor − Foreground color of the highlight region when the widget has focus.
- selectbackground − Background color for the selected items of the widget.
- selectforeground − Foreground color for the selected items of the widget.
from tkinter import *
main = Tk()
main.geometry("200x100")
B = Button(main, width = 10, height=5, text = "Hello", activebackground ="red", background ="yellow", foreground ="#0000ff")
B.pack()
main.mainloop()
Python tkinter more examples
Fonts
import tkinter
from tkinter.font import Font
main = tkinter.Tk()
main.geometry("200x100")
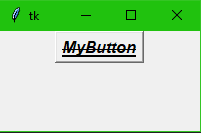
myfont = Font (family ="Helvetica", size=12, weight = "bold", slant = "italic", underline = 1, overstrike = 1 )
B = tkinter.Button(main, font = myfont, text = "MyButton")
B.pack()
main.mainloop()
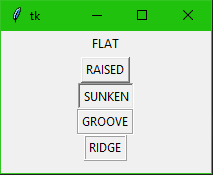
Relief
from tkinter import * main = Tk() Btn1 = Button(main, text ="FLAT", relief=FLAT ) Btn2 = Button(main, text ="RAISED", relief=RAISED ) Btn3 = Button(main, text ="SUNKEN", relief=SUNKEN ) Btn4 = Button(main, text ="GROOVE", relief=GROOVE ) Btn5 = Button(main, text ="RIDGE", relief=RIDGE ) Btn1.pack() Btn2.pack() Btn3.pack() Btn4.pack() Btn5.pack() main.mainloop()
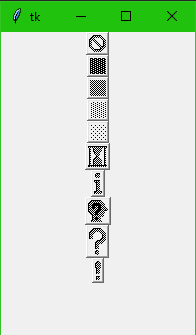
Bitmaps
from tkinter import * main = Tk() MyButtonsLists = ["error","gray75","gray50","gray25","gray12", "hourglass","info","questhead","question","warning"] for txt in MyButtonsLists: btns = Button(main, text= txt, bitmap= txt) btns.pack() main.mainloop()
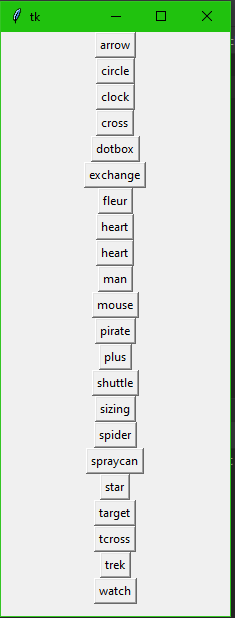
Cursors
from tkinter import * main = Tk() MyButtonsLists = ["arrow", "circle", "clock", "cross", "dotbox", "exchange", "fleur", "heart", "heart", "man", "mouse", "pirate", "plus", "shuttle", "sizing", "spider", "spraycan", "star", "target", "tcross", "trek", "watch"] for txt in MyButtonsLists: btns = Button(main, text = txt, cursor = txt) btns.pack() main.mainloop()
Button
from tkinter import * top = Tk() B = Button(top, text ="Hello") B.pack() B.place(bordermode=OUTSIDE, height=100, width=100) top.mainloop()
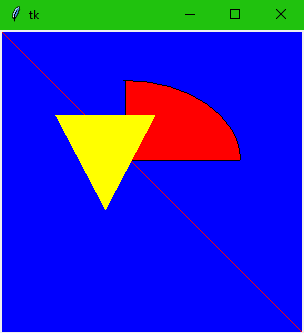
Canvas
import tkinter main = tkinter.Tk() canvas = tkinter.Canvas(main, bg="blue", height=300, width=300) chord = 10, 50, 240, 210 #X1, Y1, X2, Y2 canvas.create_arc(chord, start=0, extent=90, fill="red") canvas.create_line(0, 0, 400, 400, fill="red") canvas.create_polygon(55, 85, 155, 85, 105, 180, 55, 85, fill = "yellow") canvas.pack() main.mainloop()
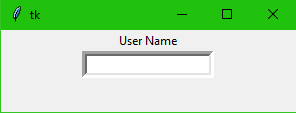
Entry
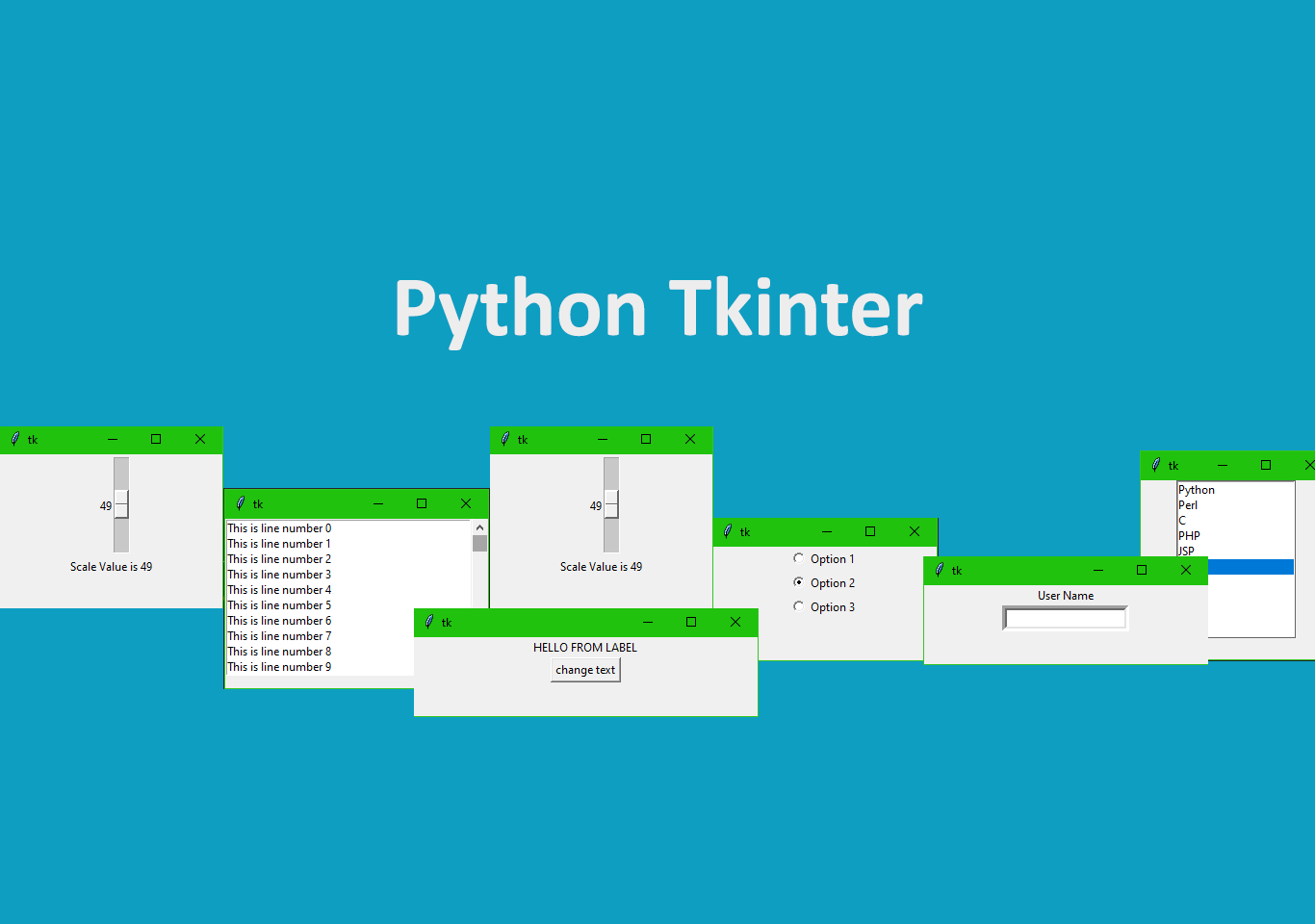
from tkinter import * main = Tk() label = Label(main, text="User Name") label.pack() entry = Entry(main, bd =5) entry.pack() main.mainloop()
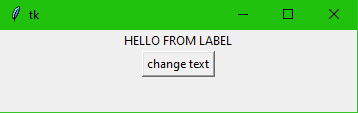
Label
from tkinter import *
root = Tk()
label = Label( root, text = "HELLO FROM LABEL" )
label.pack()
def settext(val):
label["text"] = val
btn = Button (root, text= "change text", command = lambda: settext("Changed text"))
btn.pack()
root.mainloop()
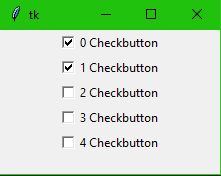
Check button
from tkinter import * main = Tk() for x in range(5): checkBtns = Checkbutton(main) checkBtns["text"] = str(x) + " Checkbutton" checkBtns.pack() main.mainloop()
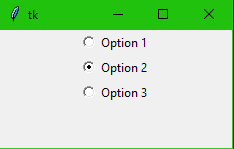
Radio button
from tkinter import * root = Tk() var = IntVar() Rbutton1 = Radiobutton(root, text="Option 1", variable=var, value=1) Rbutton1.pack() Rbutton2 = Radiobutton(root, text="Option 2", variable=var, value=2) Rbutton2.pack() Rbutton3 = Radiobutton(root, text="Option 3", variable=var, value=3) Rbutton3.pack() root.mainloop()
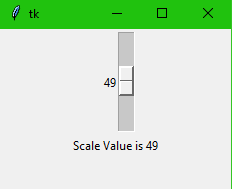
Scale
from tkinter import *
root = Tk()
def setscalevalue(val):
var2.set("Scale Value is {0}".format(var.get()))
var = IntVar()
var2 = StringVar()
scale = Scale( root, variable = var, command = setscalevalue )
scale.pack()
label = Label(root, textvariable = var2)
label.pack()
root.mainloop()
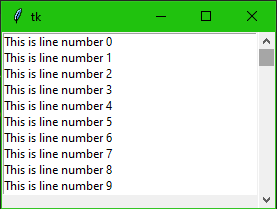
Scrollbar
from tkinter import * root = Tk() scrollbar = Scrollbar(root) scrollbar.pack( side = RIGHT, fill = Y ) mylist = Listbox(root, yscrollcommand = scrollbar.set) for line in range(100): mylist.insert(line, "This is line number " + str(line)) mylist.pack( fill = BOTH ) scrollbar.config( command = mylist.yview ) mainloop()


I was recommended this website by my cousin I am not sure whether this post is written by him as nobody else know such detailed about my difficulty You are wonderful Thanks
Fantastic beat I would like to apprentice while you amend your web site how could i subscribe for a blog site The account helped me a acceptable deal I had been a little bit acquainted of this your broadcast offered bright clear concept