Introduction
A Python passcode generator is a practical, beginner-friendly project that demonstrates how software can generate strong, unpredictable credentials. The project generates ready-to-use credentials.
A passcode generator is a software program designed to create random passwords using sequences of characters used for authentication purposes. These sequences can be numeric PINs, alphanumeric passwords, or complex strings containing symbols. The primary goal of a passcode generator is to produce credentials that are difficult to guess, brute-force, or predict. According to cybersecurity research, weak or reused passwords remain one of the leading causes of data breaches worldwide, making automated passcode generation a critical security practice rather than a convenience.
The stronger a passcode is, the more secure your data becomes. In today’s digital environment, nearly every service, device, and platform depends on passcodes for protection. When a passcode is weak or easy to guess, it becomes a direct entry point for attackers, putting personal and sensitive information at serious risk of being stolen or misused. This is why relying on simple or predictable passcodes is no longer safe.
To help users understand passcode strength, several online passcode-checking tools are available. These platforms analyze how strong a passcode is and estimate the amount of time required to crack it using common attack methods. Popular examples, Password meter, online domain tools, my1login.com, etc, and many more.
Why choose Python?
Python is widely regarded as one of the best languages for beginners and security enthusiasts alike. Its simple syntax, readability, and extensive standard library make it particularly suitable for building utilities like a passcode generator. Python includes built-in modules that support randomization and secure number generation, allowing developers to focus on logic rather than low-level complexity. This is one of the reasons Python is frequently used in cybersecurity tooling, automation scripts, and educational projects
Code Explanation
1. Character Pools (Building Blocks)
letters = ['a', 'b', ..., 'Z']
numbers = ['0', '1', ..., '9']
symbols = ['!', '#', '$', '%', '&', '(', ')', '*', '+']
These three lists define where the passcode characters come from.
- letters contain lowercase and uppercase alphabets
- numbers contain digits 0–9
- symbols contains special characters
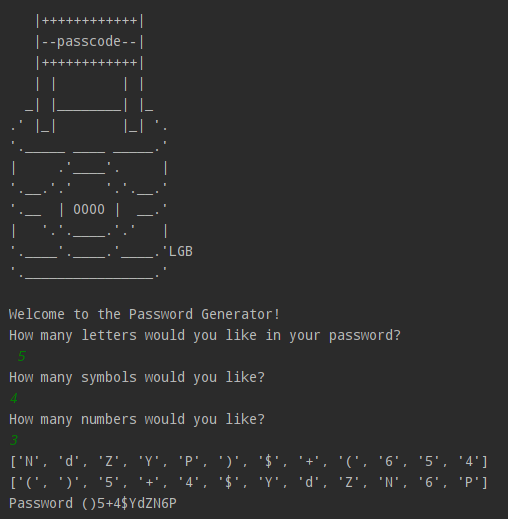
2. ASCII Art
print("""
|++++++++++++|
|--passcode--|
|++++++++++++|
| | | |
_| |________| |_
.' |_| |_| '.
'._____ ____ _____.'
| .'____'. |
'.__.'.' '.'.__.'
'.__ | 0000 | __.'
| '.'.____.'.' |
'.____'.____.'____.'LGB
'.________________.'
""")
This block prints ASCII art to the terminal.
- It does not affect logic
- Used only for visual appeal
- Common in beginner CLI projects to improve user experience
3. User Interaction
print("Welcome to the Passcode Generator!")
nr_letters = int(input("How many letters would you like in your Passcode?\n"))
nr_symbols = int(input("How many symbols would you like?\n"))
nr_numbers = int(input("How many numbers would you like?\n"))
Here is the program:
- Prompts the user for how many letters, symbols, and numbers
- Converts input strings into integers using
int()
This allows the user to customize passcode length and strength.
4. Passcode Container (Initialization)
Passcode_list = []
This empty list will temporarily store all selected characters before shuffling.
Why a list?
- Strings in Python are immutable
- Lists allow easy shuffling and appending
5. Random Letter Selection
for char in range(1, nr_letters + 1):
Passcode_list.append(random.choice(letters))
This loop:
- Runs
nr_letterstimes - Picks one random letter each iteration
- Adds it to
Passcode_list
random.choice() selects one element randomly from the list.
import random
Without this, the program will raise a name error
6. Random Symbol Selection
for char in range(1, nr_symbols + 1):
Passcode_list += random.choice(symbols)
This adds symbols to the passcode list.
However:
+=With a string adds each character individually- It works here only because symbols are single characters
Better practice would be:
Passcode_list.append(random.choice(symbols))
Your code works, but it’s fragile and misleading.
7. Random Number Selection
for char in range(1, nr_numbers + 1):
Passcode_list += random.choice(numbers)
Same logic as symbols:
- Random digits are selected
- Added to the list
Again, this works by accident, not by design.
8. Debug Output
print(Passcode_list)
This prints the passcode before shuffling, which means:
- Letters come first
- Symbols come next
- Numbers come last
This is predictable and insecure.
9. Shuffling for Security
random.shuffle(Passcode_list)
This is a critical security step.
- Randomizes character order
- Prevents pattern-based guessing
- Makes the passcode much stronger
Without this, your passcode would be weak.
10. Debug Output (After Shuffle)
print(Passcode_list)
Now the order is fully randomized.
Good for testing, bad for production (leaks secrets).
11. Convert List to String
Passcode = ""
for char in Passcode_list:
Passcode += char
This loop:
- Starts with an empty string
- Appends each character
- Builds the final passcode
This step is necessary because:
- Lists cannot be used as passwords
- Authentication systems expect strings
12. Final Output
print(f"Passcode {Passcode}")
Displays the generated passcode to the user.
Passcode generator source code
letters = ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'f', 'g', 'h', 'i', 'j', 'k', 'l', 'm', 'n', 'o', 'p', 'q', 'r', 's', 't', 'u', 'v', 'w', 'x', 'y', 'z', 'A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E', 'F', 'G', 'H', 'I', 'J', 'K', 'L', 'M', 'N', 'O', 'P', 'Q', 'R', 'S', 'T', 'U', 'V', 'W', 'X', 'Y', 'Z']
numbers = ['0', '1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9']
symbols = ['!', '#', '$', '%', '&', '(', ')', '*', '+']
print("""
|++++++++++++|
|--passcode--|
|++++++++++++|
| | | |
_| |________| |_
.' |_| |_| '.
'._____ ____ _____.'
| .'____'. |
'.__.'.' '.'.__.'
'.__ | 0000 | __.'
| '.'.____.'.' |
'.____'.____.'____.'LGB
'.________________.'
""")
print("Welcome to the Passcode Generator!")
nr_letters= int(input("How many letters would you like in your Passcode?\n"))
nr_symbols = int(input(f"How many symbols would you like?\n"))
nr_numbers = int(input(f"How many numbers would you like?\n"))
Passcode_list = []
# passcode generator
for char in range(1, nr_letters+1):
Passcode_list.append(random.choice(letters))
for char in range(1, nr_symbols+1):
Passcode_list += random.choice(symbols)
for char in range(1, nr_numbers + 1):
Passcode_list += random.choice(numbers)
print(Passcode_list)
random.shuffle(Passcode_list)
print(Passcode_list)
Passcode = ""
for char in Passcode_list:
Passcode += char
print(f"Passcode {Passcode}")
How to use this passcode generator?
- Copy the code to your editor.
- Execute the passcode generator project.
- Use the Passcode.