Introduction
The Guess the Door game in Python is a simple, interactive command-line project designed to strengthen your understanding of programming logic, user input handling, and decision-making structures.
Guess the door game is a remarkable and fun game. It is an AI based game which is played against a computer. The project uses python version 3 as python interpreter. Guess the Door is a text-based logic story game inspired by classic probability and choice-based puzzles. The player is typically shown two or three doors. Only one door is correct, and choosing the wrong door ends the game or triggers a retry.
The game works entirely through logical decisions. The system compares the user’s choice against a predefined or randomly selected correct option. If the choice matches, the player wins. If not, the game responds with a failure message and may offer another attempt. This structure mirrors real-world applications such as login validation, menu navigation, and decision trees. That is why the guess the door project is commonly used in beginner Python tutorials and learning platforms.
From a learning perspective, Guess the Door is valuable because it helps beginners understand how programs interact with users. It introduces key programming ideas such as user input handling, conditional statements, and control flow. The developer must clearly define rules: how many doors exist, what happens on a wrong choice, and whether the player can retry. This trains beginners to think step by step and translate real-world logic into program behavior.
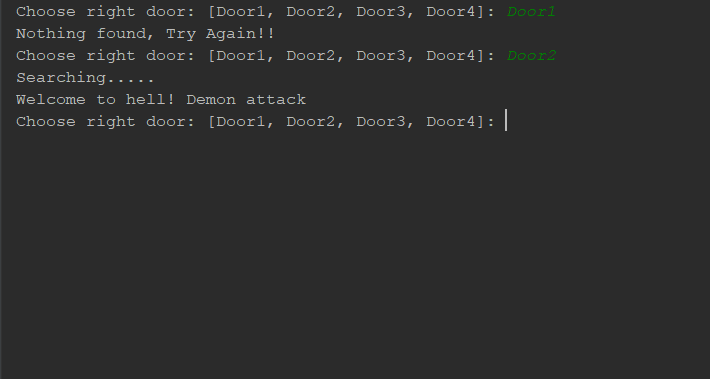
Core Game Logic
- The program defines a correct door.
- The user is asked to choose a door.
- The program evaluates the choice.
- A result is displayed based on correctness.
- The game either ends or restarts.
Building the project
The Guess the Door project is built using simple yet powerful Python concepts that help beginners understand how real programs work behind the scenes. The project is divided into multiple functions to keep the logic clean, readable, and easy to manage. When the user selects a door, the program compares that input with a randomly chosen door by the computer and then displays the result instantly.
The project structure usually contains two main files:init file and the doors file. The init file is responsible for initializing the program structure. It allows the class to be treated as a package and helps set up initial attributes when an object is created. This introduces beginners to how Python organizes projects and manages classes in a structured way, which is an essential real-world skill.
User interaction is handled using the input mechanism, which allows players to make choices during gameplay. To keep the game unpredictable and fair, Python’s random functionality is used to select the winning door. Decision-making is controlled using conditional logic, where the program checks whether the user’s choice matches the system’s choice and responds accordingly.
Even though the project uses important concepts like functions, condition checks, and external libraries, the overall codebase remains short and beginner-friendly. This makes it ideal for learners who want to practice reading, understanding, and modifying Python programs without feeling overwhelmed. Working on this project helps beginners improve logical thinking, understand file structure, and gain confidence in writing functional Python programs. By downloading and experimenting with the code, learners can tweak the rules, add features, and strengthen their problem-solving skills.
Why beginners should not skip?
Many beginners underestimate small projects like Guess the Door and rush toward advanced frameworks or complex applications. This is a mistake. Skipping foundational projects slows long-term progress and creates weak understanding that surfaces later as confusion and frustration. Guess the Door may look simple, but it trains skills that every programmer must master.
First, this project forces beginners to think logically, not just write syntax. You must decide how the game starts, how choices are evaluated, and how the program responds to success or failure. This kind of step-by-step reasoning is the backbone of real software development. Without it, learners often rely on copying code without understanding why it works.
Second, Guess the Door teaches user input handling and validation. Beginners quickly realize that users do not always behave as expected. Learning how to handle incorrect or unexpected input early builds habits that are essential for writing reliable programs later, such as command-line tools, web forms, or APIs.
Third, the project introduces program flow control in a practical way. Concepts like conditional logic and repetition stop being abstract ideas and become tools that control the game’s behavior. This practical exposure makes future topics easier to understand, including automation scripts and backend logic.
How to use this project?
- Install Python version 3.
- Download the project.
- Set up an editor or IDE. (vs code, sublime text, atom)
- Open the python file in an editor.
- Execute the program.
- Start using project.
- Enjoy!
If you are serious about learning Python, do not just read about the Guess the Door project build it. Change the number of doors, add retries, or modify the rules to see how the game behavior changes. This hands-on experimentation is where real learning happens.
Download the project files, run the program, and spend time understanding how each part works.


