Introduction
The OSI reference model is a fundamental concept in computer networking. It not only helps in understanding how data flows through a network but also aids in diagnosing problems, securing infrastructure, and designing scalable systems.
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) produced the OSI (Open Systems Interconnection) Reference Model in 1984. It divides the functions of a telecommunications or computing system into seven distinct layers, each of which is responsible for a certain component of data transmission. The OSI model encourages interoperability between different systems and acts as a reference tool for network design and troubleshooting.
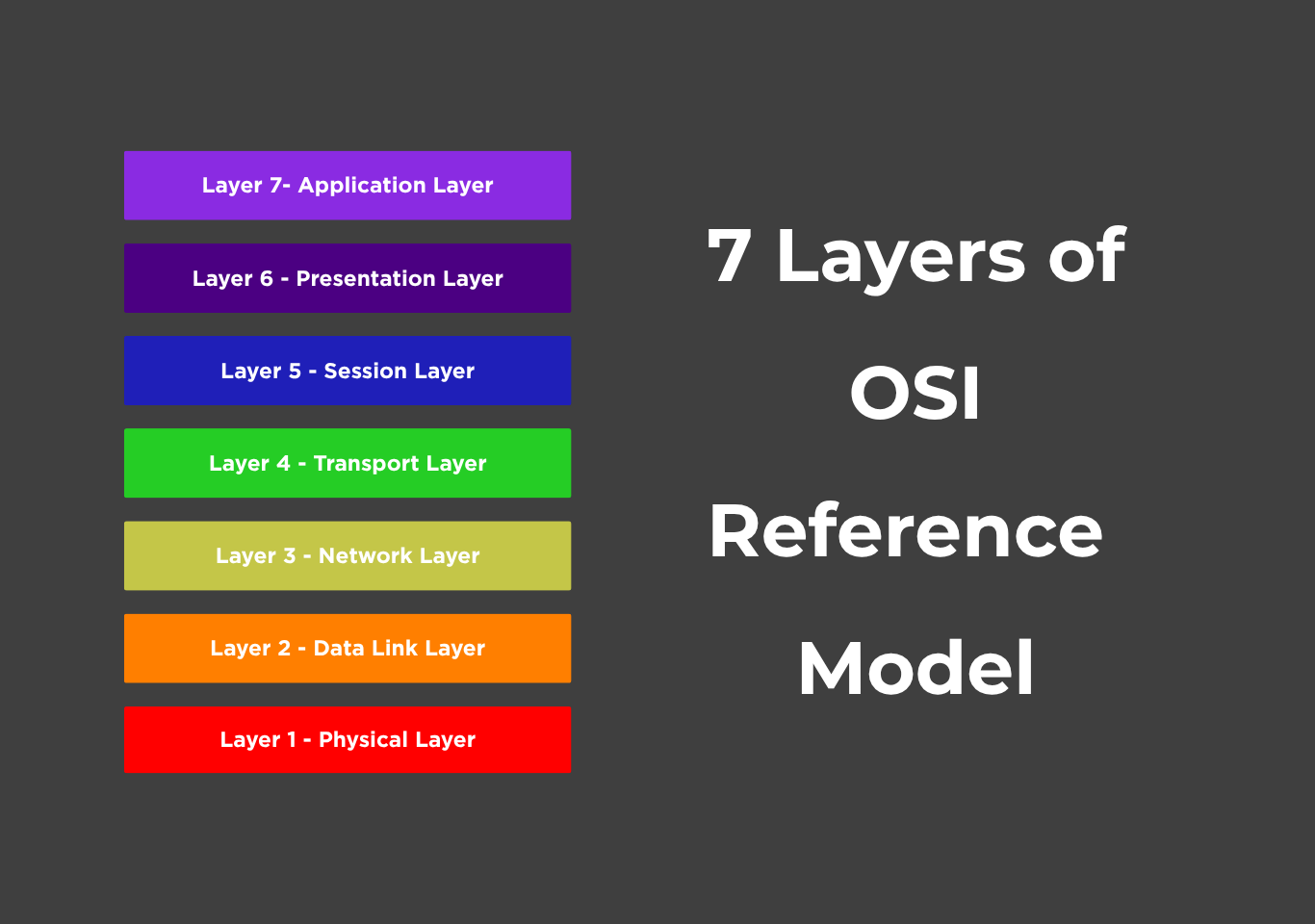
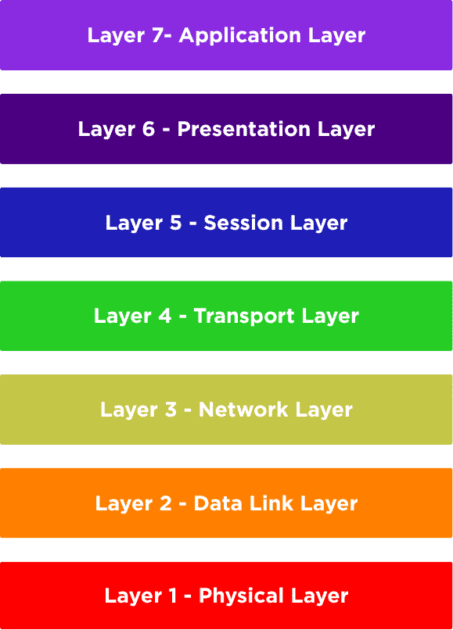
From bottom to top, the layers of OSI reference model are Physical, Data Link, Network, Transport, Session, Presentation, and Application. Each layer serves the layer above it while also being served by the layer beneath it. For example, the Transport Layer (Layer 4) assures consistent data transfer and flow control, whereas the Network Layer (Layer 3) manages routing and IP addressing.
Although the TCP/IP model is now more generally used in real-world networking, the OSI model remains popular in teaching, documentation, and network protocol research due to its clarity and modularity.
The paradigm is particularly beneficial for troubleshooting since it allows IT workers to identify issues layer by layer, from physical hardware failures to application-level defects. It also plays an important role in network security, allowing different protection measures to be implemented at each tier.
Purpose and Importance of the OSI Reference Model
The OSI model’s principal goal is to help vendors and developers design network-compatible technologies. It aids in viewing how data flows from one machine to another and identifying potential issues.
Key objectives of the OSI Model:
- Establish a framework for developing open communication systems.
- Allow compatibility between various hardware and software systems.
- Define distinct layers and functionalities in a network.
- Simplify the troubleshooting and development processes.
- Educate students and professionals about network communication.
The Seven Layers of the OSI Reference Model
The OSI reference model consists of seven layers, each with specific functions and responsibilities. These layers are ordered from the lowest (closest to the hardware) to the highest (closest to the user):
Layer 7 – Application Layer
The Application Layer is the closest to the end user. It provides network services to applications and enables user interaction with the network.
Layer 6 – Presentation Layer
The Presentation Layer translates the data format from sender to receiver. It also handles data encryption and compression.
Layer 5 – Session Layer
The Session Layer manages and controls connections between computers. It establishes, maintains, and terminates sessions.
Layer 4 – Transport Layer
The Transport Layer ensures end-to-end communication, reliability, and proper sequencing of data. It segments large data into manageable pieces.
Layer 3 – Network Layer
The Network Layer manages the routing of data between devices across different networks. It determines the best path for data transmission.
Layer 2 – Data Link Layer
The Data Link Layer handles node-to-node data transfer and error correction for frames. It ensures that data is transferred reliably over the physical medium.
Layer 1 – Physical Layer
The Physical Layer is the foundation of the OSI reference model. It is responsible for the actual transmission of raw binary data over physical media such as cables, radio frequencies, or optical signals.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages of OSI reference model
- The OSI model defines a standardized framework for networking that encourages interoperability among various systems and devices.
- Its tiered architecture enables separate development and upgrades at each layer without influencing the others.
- The OSI model is commonly used in education to assist students comprehend network communications step by step.
- It enables vendor-neutral communication, making it easier to combine products from many hardware and software suppliers.
- It facilitates systematic troubleshooting by allowing engineers to identify network problems layer by layer.
- The OSI model assists in implementing suitable security mechanisms at various layers, hence improving overall network protection.
Disadvantages of OSI reference model
- The OSI model is primarily theoretical and is not widely adopted as an implementation standard in real-world networks.
- It may provide additional overhead due to the rigorous separation of functions into seven layers.
- The TCP/IP model is used in the majority of real-world networks, making OSI less applicable to modern internet architecture.
- OSI was designed after TCP/IP became extensively established, which limited its real-world application.
- In practice, some protocols cross multiple OSI levels, testing the model’s rigid layer boundaries.