Introduction
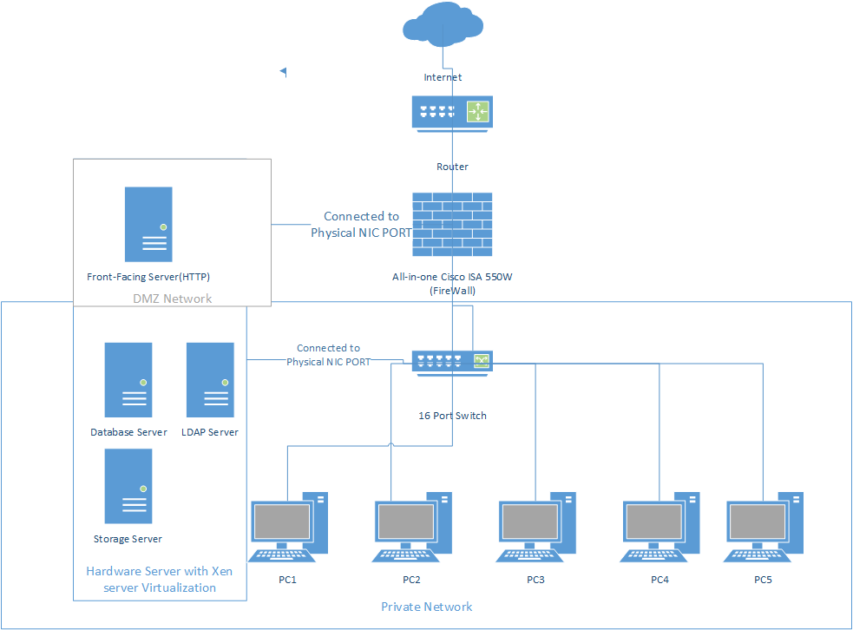
Network architecture is the network structure interaction between networking devices, services and client s to meet their connectivity requirements.
Network architecture encompasses the structural and logical layout of networks, detailing how devices are connected and the protocols that govern data transfer between them. It describes how the network devices are connected and data transfer between them. Network design includes features such as DNS and DHCP to meet the demands of individual clients.
It encompasses a variety of forms, including Wide-Area Networks (WANs), which allow users to connect to resources over long distances, Access networks, which provide intra-office communication, and Data Center Networks, which host applications and enable data access. Each architecture type is unique, with particular network security considerations, connectivity requirements, and service provisions.
Because network architecture can either improve or degrade system performance, it is essential to plan it out. Network slowdowns might result, for example, from selecting the incorrect transmission media or equipment for a certain anticipated server load. Additionally, network architecture can help with security, which is becoming more and more crucial as more consumer devices connect to the network.
Network architecture importance
- Maximize network availability
- Enabling efficient data transfer
- Securing essential data and assets
- Reducing expensive cost
- Supporting business resiliency
Types of network architecture
Client server architecture
In this architecture, a powerful computer acts as a server while other computes work as a client. Every computer access data from the server. In client/server networks, all files and directories are managed by the server and requests for data or communication with other users must pass through the server.
Peer to peer architecture
Without the need for a single centralized server, computers are connected to one another and resources are dispersed across all network nodes in the peer-to-peer (P2P) network paradigm. Every machine or node in the network has the ability to function as a client and a server, sharing or seeking resources from other nodes at different times.
Hybrid architecture
By combining the best aspects of both client/server and peer-to-peer network architectures, hybrid networks are able to overcome their respective shortcomings. The integration of dispersed networks and centralized servers into a unified architecture can facilitate more economical scaling, improved fault tolerance, and better allocate resources.
Cloud based architecture
A cloud-based network architecture incorporates cloud infrastructure and services, enabling flexible and on-demand access to servers, compute resources, data storage, and virtualization capabilities delivered over the Internet.



Techno rozen I very delighted to find this internet site on bing, just what I was searching for as well saved to fav
Thank you for your comment.
Mygreat learning I just like the helpful information you provide in your articles
Ny weekly I’m often to blogging and i really appreciate your content. The article has actually peaks my interest. I’m going to bookmark your web site and maintain checking for brand spanking new information.
Thank you
Olá, boa postagem, há um problema com seu site no Internet Explorer. Gostaria de testar este IE, ainda é o líder do mercado e uma boa parte de outras pessoas ignorará sua magnífica escrita devido a esse problema