Introduction
Lean Development is a software development approach that focuses on providing maximum value to the client while reducing waste throughout the development process. It is a part of an agile methodology
Lean encourages high-quality software development by offering value early and often, empowering teams, and constantly improving. At its foundation, Lean Development enables teams to build only what they need, deploy it quickly, and continuously adapt their approach based on feedback. It promotes tiny, incremental releases that can be evaluated and improved in short cycles, lowering the danger of adding unneeded or undesirable features.
Lean Development is very effective in dynamic circumstances where the client’s needs change quickly. It promotes agility by focusing on results rather than inflexible procedures. By decreasing waste, empowering teams, and focusing on value, Lean allows for faster delivery, higher quality, and better alignment with customer expectations. Lean Development, whether applied alone or in conjunction with Agile or DevOps approaches, is an effective methodology for modern, efficient, and user-centered software development.
History of lean development
The history of Lean Development may be traced back to the Lean Manufacturing movement, namely the Toyota Production System (TPS), which was established in post-war Japan. In the 1940s and 1950s, Toyota engineers, especially Taiichi Ohno, pioneered strategies for increasing efficiency, reducing waste, and optimizing production flow with limited resources. These approaches stressed Kaizen (continuous improvement), just-in-time (JIT) manufacturing, and worker respect, which became the key concepts of Lean Manufacturing.
James P. Womack and Daniel T. Jones popularized the term “Lean” in the 1990s with their book Lean Thinking, which distilled manufacturing ideas into a broader management philosophy. As software development progressed in the late 1990s and early 2000s, practitioners began to see similarities between industrial inefficiencies and common software development concerns such as overengineering, bloated requirements, and extended delivery cycles. This discovery prompted the application of Lean principles to the domain of software.
Mary and Tom Poppendieck’s key work, Lean Software Development: An Agile Toolkit, was published in 2003, translating Lean Manufacturing concepts into software development processes. They introduced seven Lean principles designed specifically for software: remove waste, include quality, generate knowledge, delay commitment, deliver quickly, respect people, and maximize the entire. Lean Development gained further traction alongside the Agile movement, especially as software companies sought faster, more flexible, and customer-focused delivery methods.
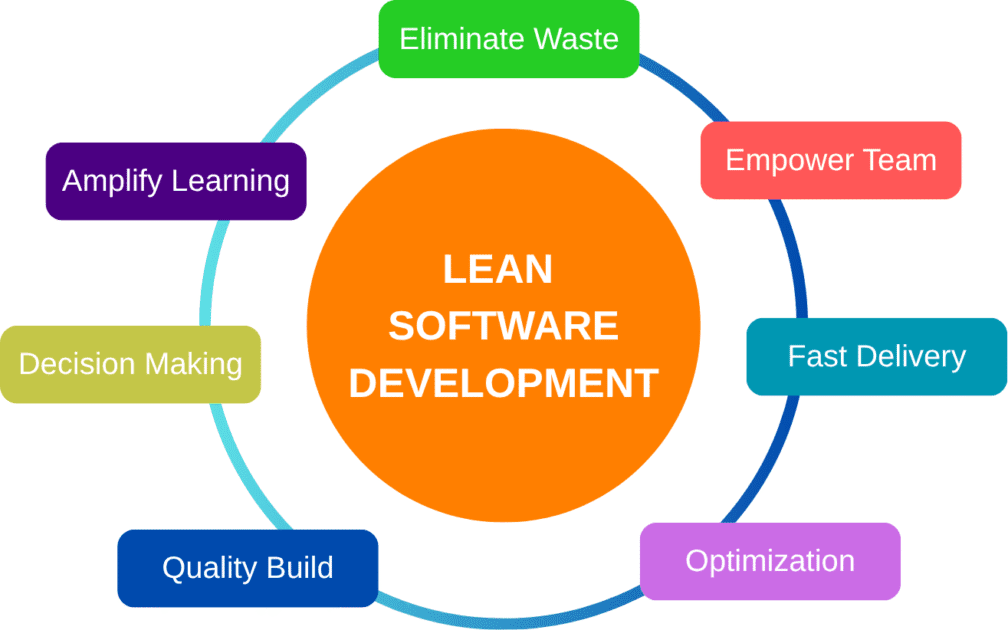
Core principles of lean development
- Waste Elimination
- Amplifying Learning
- Late Decision Making
- Fast Delivery
- Team Empowerment
- Built-in Integrity
- View Applications as a Whole
Development phases of lean development
Identify value
The first step focuses on determining what truly provides value to the client. This entails consulting with stakeholders, customers, and product owners to determine which features or results are most important. Teams question themselves, “What problems are we solving?” What do users need? Any activity that does not directly add to its value is considered wasteful. This phase ensures that corporate goals and user needs are aligned, allowing teams to focus on high-impact activities. Clear communication, user research, and early feedback are crucial in this process. By precisely identifying value, teams can avoid overbuilding, minimize needless features, and guarantee that each work adds to customer happiness and corporate success.
Map the value
This step entails visualizing the complete workflow from inception to delivery, typically using a Value Stream Map. The goal is to identify each step in the development process—idea generation, coding, testing, and deployment—and determine which adds value and which causes delays or waste. This mapping helps to identify bottlenecks, redundancies, and handoff difficulties. By making the workflow accessible, teams can start optimizing it. It also encourages cross-departmental collaboration, ensuring that no aspect of the system runs alone. Finally, mapping the value stream results in a more predictable, efficient, and transparent development process, which is consistent with Lean’s goal of providing customer value fast and efficiently.
Create flow
After identifying and optimizing the value stream, the next goal is to create a seamless, continuous workflow. This entails minimizing delays, interruptions, and context changes throughout development. Teams seek to remove bottlenecks, automate repetitive activities, and ensure that work flows smoothly from one phase to the next. Visual tools like as Kanban boards are frequently used to track progress and limit Work in Progress (WIP), hence improving focus and throughput. Creating flow increases cycle time and responsiveness while minimizing developer irritation. It also encourages collaboration because everyone can readily monitor the status of tasks. A well-maintained flow guarantees that valuable features are given consistently and predictably to end users.
Establish pull
In this phase, work is started based on demand rather than following a set schedule. Teams “pull” additional work only when they have the capacity, avoiding overburden and increasing focus. This is in contrast to traditional methods, which assign significant amounts of labor up front, sometimes resulting in delays and poor quality. The pull method ensures that resources are only used when necessary, and activities are completed precisely in time, increasing efficiency. It also supports better prioritizing because teams are continually focused on what will add the most value next. This method ensures that the development process remains lean, responsive, and adaptable to changing client needs or market expectations.
Pursue perfection
Lean Development is never “done”; it requires an attitude of continual improvement. This phase focuses on Kaizen, in which teams periodically reflect on their processes through retrospectives, reviews, and metric analysis. The idea is to find minor, incremental adjustments that can help decrease waste, increase speed, or improve quality. Customers, stakeholders, and team members provide valuable feedback to help lead these developments. This phase also promotes a culture of learning, experimentation, and adaptability. Teams improve their ability to deliver value over time by continuously developing their tools, tactics, and communication. Pursuing perfection guarantees long-term viability, team development, and continuous alignment with changing user expectations and company goals.
When to use lean development?
- When you don’t have enough resources.
- When you need more information.
- When your project needs to be finished in short time.
- When you have a low budget.
Benefits and Drawbacks
Benefits
- Faster time-to-market
- The product is developed in a short period with a limited budget.
- Improved product quality
- Customer-centric approach
- Enhanced team collaboration
- Increased flexibility and adaptability
- Continuous improvement culture
- Lean eliminates waste within a production facility.
Drawbacks
- Difficult to measure waste and value
- Requires a significant culture shift
- Less suitable for fixed-scope projects
- Lack of a prescriptive framework
- High dependency on team discipline and maturity
- The project is highly dependent on team members.
- Developers must understand the customer requirements.


