Introduction
Feature Driven Development (FDD) is an iterative and incremental software development process that focuses on features with business value. It follows an iterative approach for software development.
Feature Driven Development (FDD) is a client-centric, iterative Agile methodology that focuses on providing real software features in short, organized development cycles. It focuses on developing and delivering small, well-defined bits of functionality (known as “features”) that add genuine value to the user.
A feature in FDD is a tiny, measurable, client-valued function that can usually be built in a few days. Examples include “authenticate user login” and “generate monthly report.” These characteristics serve as the primary units for planning, design, development, and progress tracking in an FDD context.
Unlike other Agile approaches, such as Scrum, which are sprint-oriented, FDD encourages domain modeling and individual code ownership. To maintain accountability and an effective workflow, well-defined roles are employed, including Chief Programmer, Class Owners, Domain Experts, and Developers.
FDD has several advantages, including increased code quality, scalability for big teams, predictable delivery, and greater alignment with business goals. The process promotes frequent builds, code inspections, and continuous integration to ensure quality throughout development.
Feature driven development(FDD) is great for complicated systems or large teams that require structure while remaining agile. It works especially well when explicit business requirements are given and consistency across multiple contributors is required.
FDD in agile encourages status reporting at all levels, which helps to track progress and results. This approach allows teams to update the project regularly and identify errors quickly. The general objective of feature driven development is to deliver concrete and flexible software in a short time. Its greatest advantage is that the process is scalable even for large teams.
History of feature driven development (FDD)
Jeff De Luca coined the term “Feature Driven Development” (FDD) in 1997 while working on a large and complex software project for a Singapore-based bank, United Overseas Bank. The project’s size and complexity necessitated an organized strategy that could adapt to changing needs. De Luca worked with Peter Coad, a well-known expert in object-oriented design, to create a system that combined robust modeling with iterative, feature-based development.
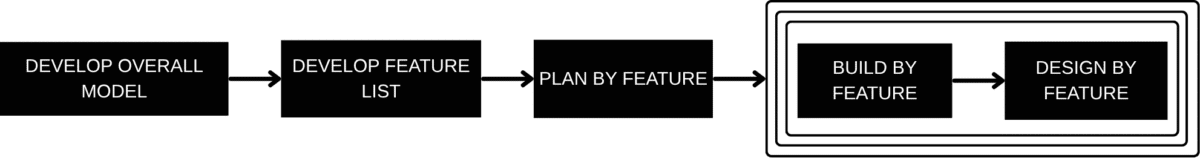
The goal was to increase predictability, maintain high quality, and prioritize delivering genuine, client-valued functionality. This resulted in the establishment of FDD’s fundamental processes, which include generating an overall model, creating a feature list, planning by feature, designing by feature, and constructing by feature.
Coad, De Luca, and others published “Java Modeling in Color with UML” in 1999, which defined and documented feature driven development (FDD). This book describes how the FDD paradigm combined object-oriented modeling (UML), agile practices, and iterative development. The use of color-coded classes and visual modeling assisted development teams in better understanding and organizing complicated domains.
When the Agile Manifesto was released in 2001, feature driven development was regarded as one of the first agile approaches, alongside Scrum, Extreme Programming (XP), and Crystal. Though not as extensively used as Scrum, Feature driven deevelopment FDD has gained appeal in areas that require high reliability, such as banking, telecommunications, and corporate software development.
Development phases of feature driven development
Develop the overall model
During this phase, your team works with domain experts and stakeholders to develop a high-level, shared Domain Object Model (DOM) for the issue space. This includes walkthroughs, analysis of older systems, and modeling sessions. Small groups create models for specific subdomains, which are subsequently combined into a cohesive overall model. Before any code is developed, early modeling establishes the architectural basis and ensures that everyone is on the same page about scope, vocabulary, and essential business activities.
Build the feature list
Using the domain model as a basis, create a thorough feature list of small, client-valued functions specified using “action-result-object.” Group these features into thematic feature sets depending on business area, then prioritize them based on value, risk, and reliance. This list defines scope and divides the system into digestible chunks, each of which is expected to be delivered within around two weeks.
Plan by feature
During the planning step, each feature is estimated, prioritized, and assigned. A Chief Programmer (or team leader) establishes the development sequence, assigns individual class tasks, and maps out dependencies. Plans often include rough schedules and milestones in two-week intervals. This offers openness and allows for progress tracking. Class ownership ensures accountability, and milestone monitoring provides early warning of potential delays.
Design by feature
The design phase for the chosen features has begun. The Chief Programmer directs a feature-level design walkthrough, which frequently employs UML artifacts such as sequence diagrams. Class owners make changes or additions to the DOM, and a design inspection (peer review) certifies the result. The result is a tiny, coherent design package suitable for coding, which ensures structural consistency, architectural integrity, and integration readiness.
Build by feature
Developers implement the functionality in accordance with the approved design, which includes code generation, unit testing, and code inspection. Once the feature has passed quality tests, it is incorporated into the main build. Integration tests indicate that the new code integrates flawlessly with the existing system. This phase delivers a working, tested, and shipped feature in typically less than two weeks.
When to Use Feature Driven Development
Feature driven development is best suited for:
- Large teams (10+ developers)
- Projects requiring upfront modeling
- Systems with complex business logic
- Organizations that prioritize structured processes
- Scenarios where accurate progress tracking is crucial
Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages of feature driven development
- Scalability – FDD is ideal for large teams and complex projects because of its systematic approach and explicitly defined roles.
- Predictable progress.- Tracking progress is based on finished features, providing visibility into development status and timescales.
- High code quality – Regular design and code inspections guarantee that the code is consistent, maintainable, and contains fewer bugs.
- Business-focused development – Features are tiny, client-valued functions that keep development in line with business objectives.
- Efficient delivery – Features are supplied incrementally, allowing for more regular and useful releases.
- Clear responsibilities – Chief Programmer and Class Owner roles help to clarify accountability and streamline task assignments.
- Improved Risk Management – Early domain modeling assists in identifying technical and business concerns before full development begins.
- Less Meeting Overhead – Compared to other Agile techniques, FDD places a greater emphasis on documentation and systematic planning than on daily meetings.
- Encourages reusability – The modeling method frequently produces reusable classes and components.
- Supports long-term maintenance – The feature-based design and documentation facilitate long-term system maintenance and scaling.
Disadvantages of feature driven development
- Building the model and feature list requires significant upfront work and effort.
- Not ideal for small teams – The method may be overly process-intensive for small or short-term tasks.
- Requires Success depends on qualified Chief Programmers and experienced team members.
- Limited customer involvement – Less frequent stakeholder involvement, as opposed to approaches such as Scrum, may diminish response to feedback.
- Complex feature dependencies – Managing dependencies between features can be tricky as the project grows.
- Rigid Process – The structure may limit flexibility to large changes in scope or priorities.
- Documentation Overload – The emphasis on modeling and planning can result in excessive documentation.
- Steep Learning Curve – New team members may need some time to grasp the model-driven approach and feature tracking system.
- Class Ownership Drawbacks – Individual code ownership may impede collaborative programming and pairing work.
- Model Maintenance – Keeping the domain model up to current requires ongoing effort throughout the development life cycle.

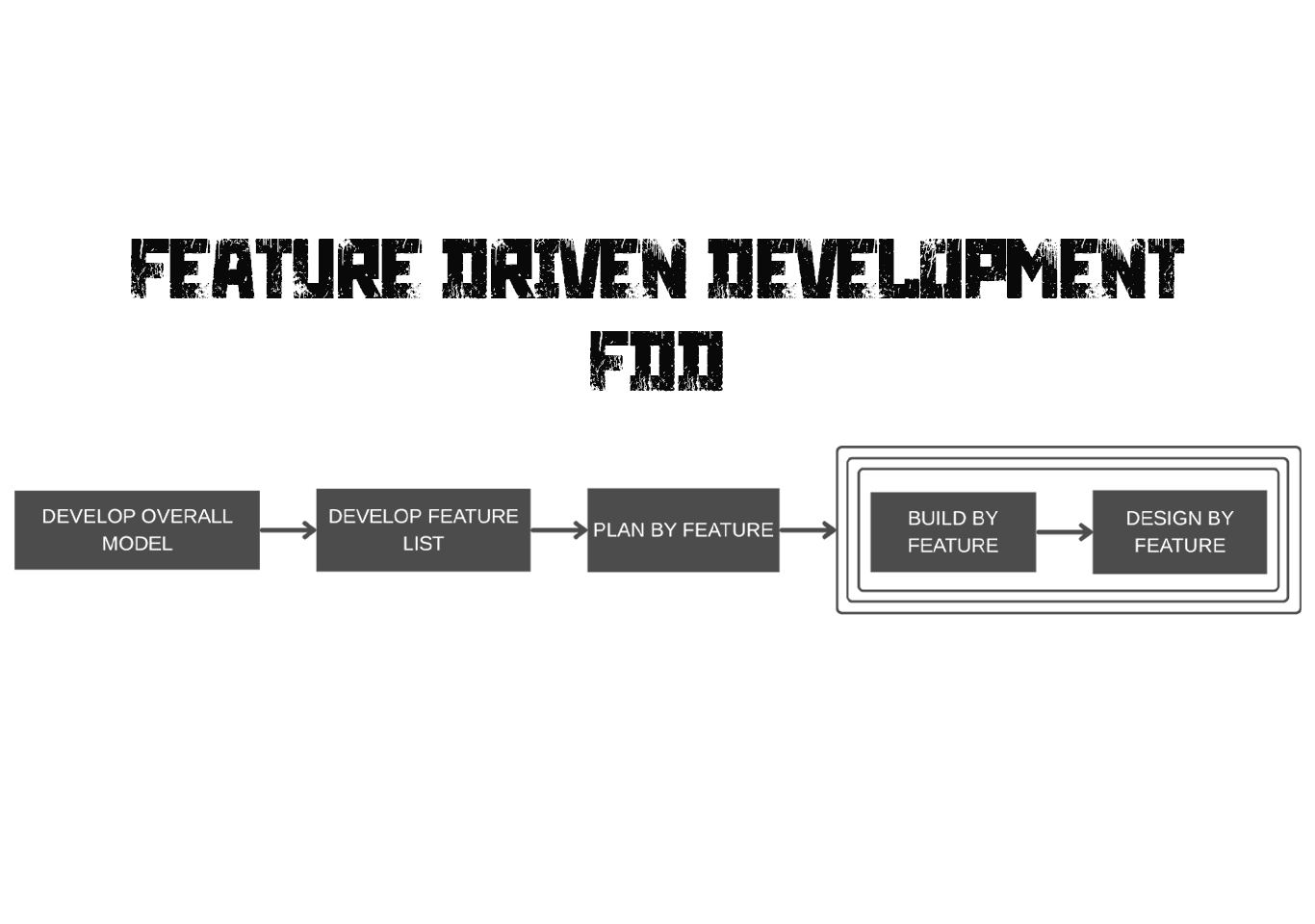
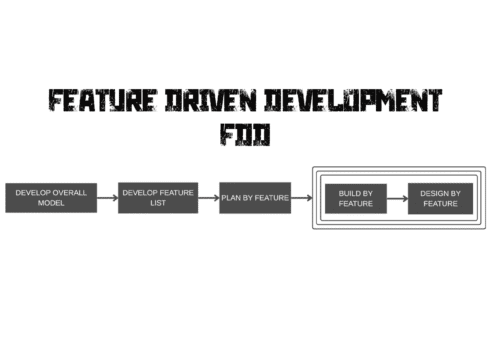
Feature Driven Development (FDD) is a client-centric, agile methodology focused on delivering tangible, working software repeatedly and on time. It emphasizes building and designing features—small, client-valued functions—which makes it a practical and scalable option for large-scale projects.When paired with Web Application Development Services , FDD ensures that every feature built aligns with user needs and business goals. This synergy leads to faster delivery cycles, better collaboration, and web apps that are both functional and user-friendly.