Introduction
An electric bill calculator is a program or tool designed to calculate the total electricity charges based on the number of units consumed during a billing period.
In the context of C programming, an electric bill calculator takes user input and calculates the bill based on the written program. It typically uses conditional statements or functions to apply different rates for various consumption slabs, for example, lower rates for the first 100 units and higher rates for additional usage. The program may also include fixed charges, service fees, and taxes to reflect real-world billing systems.
This calculator helps students and developers understand how mathematical operations, decision-making, and modular design work in C. It is also a practical example of how programming can be applied to solve everyday problems like computing household electricity bills. With enhancements, it can support multiple customers, file-based billing records, and dynamic tariff rates.
Explanation of the code
#include <stdio.h>
Header Inclusion
This includes the standard input-output library, allowing the use of printf and scanf functions.
Main Function
int main()
The entry point of the program.
Variable Declaration
int unit; float amt, total_amt, sur_charge;
unit→ Stores the number of electricity units consumed (input from user).amt→ Stores the calculated cost based on units.sur_charge→ Stores the surcharge amount.total_amt→ Stores the total bill after adding surcharge.
Input from User
printf("Enter total units consumed: ");
scanf("%d", &unit);
- Prompts the user to enter the total units consumed.
- scanf reads an integer value from the console and stores it in
unit.
Calculate Bill Based on Slab Rates
if(unit <= 50)
{
amt = unit * 0.50;
}
else if(unit <= 150)
{
amt = 25 + ((unit-50) * 0.75);
}
else if(unit <= 250)
{
amt = 100 + ((unit-150) * 1.20);
}
else
{
amt = 220 + ((unit-250) * 1.50);
}
- The program uses conditional statements to apply tiered rates:
- 0–50 units: ₹0.50 per unit.
- 51–150 units: ₹25 for first 50 units + ₹0.75 per unit for remaining units.
- 151–250 units: ₹100 for first 150 units + ₹1.20 per unit for remaining units.
- Above 250 units: ₹220 for first 250 units + ₹1.50 per unit for remaining units.
This is how slab-wise billing works in real electricity bills.
Add Surcharge
sur_charge = amt * 0.20; total_amt = amt + sur_charge;
- Calculates 20% surcharge on the calculated amount.
- Adds it amt to get the final total amount.
Output the Result
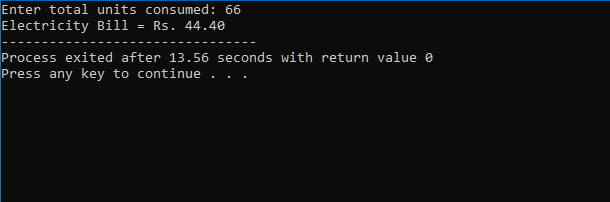
printf("Electricity Bill = Rs. %.2f", total_amt);
- Displays the total electricity bill in rupees, rounded to 2 decimal places.
End of Program
return 0;
- Terminates the program and returns control to the operating system.
Future Extensions and Improvements
- Unit tests: add automated tests for slab computation with known cases.
- File input: read multiple customer records from CSV to produce batch bills.
- GUI: integrate with GTK or a web front end for usability.
- Localization: support different currencies and decimal formats.
- More charges: add fuel adjustment, demand charge, subsidies, or time-of-use tariffs.
How to use this electric bill project?
- Copy the source code.
- Open DevC++ or any other.
- Open a new file in the editor.
- Paste the copied source code
- Compile and Execute.
- Enjoy and share.
Full source code
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int unit;
float amt, total_amt, sur_charge;
/* Input unit consumed from user */
printf("Enter total units consumed: ");
scanf("%d", &unit);
/* Calculate electric bill according to given conditions */
if(unit <= 50)
{
amt = unit * 0.50;
}
else if(unit <= 150)
{
amt = 25 + ((unit-50) * 0.75);
}
else if(unit <= 250)
{
amt = 100 + ((unit-150) * 1.20);
}
else
{
amt = 220 + ((unit-250) * 1.50);
}
/*
* Calculate total electric bill
* after adding surcharge
*/
sur_charge = amt * 0.20;
total_amt = amt + sur_charge;
printf("Electricity Bill = Rs. %.2f", total_amt);
return 0;
}
Electric bill FAQs
What is an electric bill calculator in C?
It is a C program that calculates electricity charges based on units consumed, slab rates, fixed charges, and taxes.
Can this program handle multiple customers?
The basic program handles one customer at a time. To manage multiple customers, you can use arrays or read inputs from a file.
How can I make the program more advanced?
You can add features like:
- Reading meter readings from a CSV file
- Generating bills for multiple customers
- Applying variable taxes or subsidies
- Adding a GUI interface using GTK or web front-end
Is this program suitable for real billing systems?
No. This is for learning and demonstration purposes. Real billing systems require accurate decimal handling, audit trails, and compliance with regulations.
Why use C to build an electric bill calculator?
C is fast, teaches core programming concepts, and is widely used for learning arithmetic operations, conditional logic, and modular design.