Introduction
A measuring unit convertor in C program is a classic beginner-friendly project that teaches logical structuring, user interaction, and modular programming.
A measuring unit is a simple C program that allows users to convert values from one unit to another. It takes input (the value and unit type), processes it through conversion formulas, and outputs the result. Building this project strengthens your understanding of fundamental C programming concepts. It is one of the most practical beginner-level projects used in programming courses.
You can use any type of conversion like length, weight, temperature, etc. This program focused on temperatures only. If you want to extend it you can implement other conversion units too. This article explains what a measuring unit converter in C is, how it works, its logic, benefits, real-world applications, and more.
What you learn?
- Understanding Input/Output: Learn how to take input from the user using scanf() and display results with print().
- Control Flow Mastery: Use conditions and loops to navigate options.
- Mathematical Logic: Apply formulas and conversion ratios effectively.
- Modular Programming Practice: Divide tasks into logical functions.
- Error Handling: Manage invalid inputs and ensure accuracy.
Logic behind conversion
To convert into celsius apply these formulae below.
fahrenheit = (celsius * 9 / 5) + 32; kelvin = (celsius + 273.15); rankine = (celsius + 273.15) * 1.8; reaumur = (celsius * 0.8);
Display menu
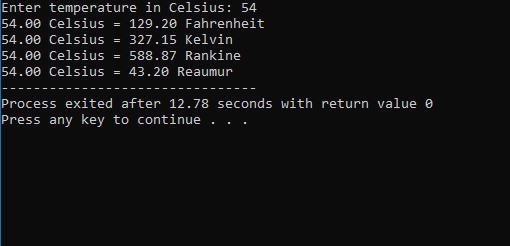
The screen demands you to input the temperature in Celsius, and rest will generate by the program.
Core Concept
The measuring unit Converter follows a three-step process:
- Input Stage: The program prompts the user to choose a conversion type (e.g., temperature, length, weight).
- Processing Stage: Based on user selection, a formula is applied to compute the converted value.
- Output Stage: The result is displayed neatly with formatted output.
Common Mistakes Beginners Make
- Forgetting to validate inputs: Entering characters instead of numbers crashes the program.
- Incorrect conversion constants: Always verify from credible sources like NIST.
- Missing default cases in switch statements: Avoid undefined behavior.
- Ignoring precision: Use float for decimal accuracy.
- No exit control: Always provide an option to terminate cleanly.
Improving the Project
You can enhance measuring unit conversion budling these.
- Build a GUI using C-based frameworks or migrate to C++.
- Store user conversions in a file using file handling.
- Accept conversions directly from terminal commands.
- Prevent invalid entries using input validation for error detection.
- Log each conversion for later reference.
Understanding the code
#include <stdio.h>
- Includes the Standard Input Output header file.
- It allows the program to use functions like printf() and scanf() for user interaction.
int main()
- Defines the main function, where program execution begins.
float celsius, fahrenheit, kelvin, rankine, reaumur;
- Declares five floating-point variables to store:
- celcius: input temperature
- fahrenheit, kelvin, rankine, reaumur: converted results
- Using float allows decimal precision (e.g., 36.5°C).
printf("Enter temperature in Celsius: ");
scanf("%f", &celsius);
- Displays a prompt for user input.
- scanf() reads the numeric value typed by the user and stores it in the variable celsius.
Conversion Formulas
fahrenheit = (celsius * 9 / 5) + 32; kelvin = (celsius + 273.15); rankine = (celsius + 273.15) * 1.8; reaumur = (celsius * 0.8); reaumur = (celsius * 0.8);
- Converts Celsius to Fahrenheit using the formula
F = (C × 9/5) + 32 - Converts Celsius to Kelvin using
K = C + 273.15 - Converts Celsius to Kelvin using
K = C + 273.15 - Converts Celsius to Rankine using
R = (C + 273.15) × 1.8
Output Section
printf("%.2f Celsius = %.2f Fahrenheit", celsius, fahrenheit);
- Prints result formatted to 2 decimal places (
%.2f). - Each result is displayed in a new line using
\n.
The four print statements output:
25.00 Celsius = 77.00 Fahrenheit 25.00 Celsius = 298.15 Kelvin 25.00 Celsius = 536.67 Rankine 25.00 Celsius = 20.00 Reaumur
return 0;
- Ends the program successfully.
- Returning
0indicates no error occurred.
Full Source Code
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
float celsius, fahrenheit, kelvin, rankine, reaumur;
printf("Enter temperature in Celsius for measuring unit: ");
scanf("%f", &celsius);
fahrenheit = (celsius * 9 / 5) + 32;
kelvin = (celsius + 273.15);
rankine = (celsius + 273.15) * 1.8;
reaumur = (celsius * 0.8);
printf("%.2f Celsius = %.2f Fahrenheit", celsius, fahrenheit);
printf("\n");
printf("%.2f Celsius = %.2f Kelvin", celsius, kelvin);
printf("\n");
printf("%.2f Celsius = %.2f Rankine", celsius, rankine);
printf("\n");
printf("%.2f Celsius = %.2f Reaumur", celsius, reaumur);
return 0;
}
How to use this project?
- Download the software Dev C++ or any other.
- Copy and paste the code above.
- Compile and execute the code.
- Convert the degree in various units.
- Extend it your own measuring unit.
- Enjoy and share.


